รูปแบบการพัฒนาหลักสูตรจากแนวคิดต่างประเทศ
รูปแบบการพัฒนาหลักสูตรตามแนวคิดของไทเลอร์
(Ralph
W. Tyler)
ไทเลอร์ได้นำเสนอแนวคิดพื้นฐานเกี่ยวกับการพัฒนาหลักสูตรและการสอนซึ่งก็คือหลักการและเหตุผลในการพัฒนาหลักสูตร(Tyler
Rationale) ว่าในการพัฒนาหลักสูตรและการสอน
ต้องตอบคำถามพื้นฐานที่สำคัญ 4 ประการ คือ (Tyler, 1949: 3)
1. จุดมุ่งหมายทางการศึกษา (Educational
Purposes) อะไรบ้างที่โรงเรียนต้องการให้ผู้เรียนได้เรียนรู้
2. ประสบการณ์ทางการศึกษา (Educational
Experiences) อะไรบ้างที่โรงเรียนจะต้องจัดให้ เพื่อช่วยให้บรรลุจุดมุ่งหมาย
3.
จะจัดประสบการณ์ทางการศึกษาอย่างไรจึงจะทำให้สอนมีประสิทธิภาพ
4.
ประเมินประสิทธิภาพของการจัดประสบการณ์การเรียนอย่างไรจึงจะทราบได้ว่าผู้เรียนได้บรรลุเป้าหมายทางการศึกษา
Tyler's concept of
curriculum development (Ralph W. Tyler)
Tyler
has introduced the basic concepts of curriculum development and instruction,
the principles and rationale for curriculum development (Tyler Rationale), in
curriculum development and instruction. There are four basic questions: (Tyler,
1949: 3)
1. What
Educational Purposes do the schools want students to learn?
2.What
educational experiences should the school provide? To help achieve the goal.
3. How will the educational
experience be taught?
4. Evaluate the effectiveness of the
learning experience. How do you know that the students have achieved their
educational goals?
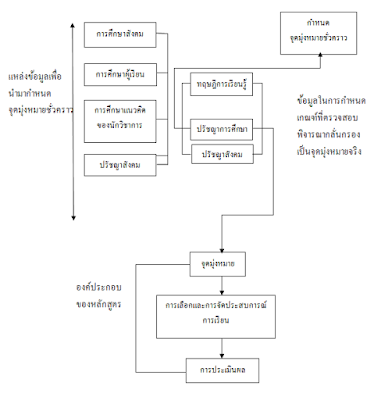
ไทเลอร์ได้วางรูปแบบโครงสร้างของหลักสูตรโดยใช้วิธีการและเป้าหมายปลายทาง
(Means
and ends approsch) ดังนี้ (วิชัย วงษ์ใหญ่, 2537: 10-11)
ในการกำหนดจุดมุ่งหมายนั้น ในขั้นแรกต้องกำหนดเป็นจุดมุ่งหมายชั่วคราวก่อน
โดยต้องนำบริบทที่เกี่ยวข้อง เช่น บริบททางด้านสังคม
ด้วยการนำสิ่งที่สังคมคาดหวังว่าต้องการให้ผู้เรียนมีคุณลักษณะอย่างไร และมีการศึกษาตัวผู้เรียน เช่น ความต้องการ
ความสนใจ ฐานะทางเศรษฐกิจของครอบครัว เป็นต้น นอกจากนั้นยังต้องศึกษาแนวคิดของนักวิชาการ
(วิชัย วงษ์ใหญ่, 2537 : 12) ความเชื่อค่านิยมของสังคมเป็นสิ่งจำเป็นที่ต้องวิเคราะห์ให้ชัดเจน เพราะการศึกษาสังคมค่านิยมขนบประเพณี
วัฒนธรรมจะให้คำตอบว่าสังคมต้องการจัดการศึกษาเพื่ออะไร
และจะจัดการศึกษาสำหรับใคร
สิ่งเหล่านี้ช่วยให้แสวงหาคำตอบที่ชัดเจนในการกำหนดเป้าหมายหรือทิศทางของการศึกษา
(ดังภาพประกอบ )
Tyler
laid out the structure of the curriculum by using the Means and ends approsch
as follows (Wichai Wongyai, 1994: 10-11).
To
set the purpose. The first step is to set a temporary goal. Relevant contexts
such as social context. What are the characteristics that society expects to
feature? In addition, the study of the concept of the scholar (Vichai Wongyai,
1994: 12) has also been studied. The belief in social values is necessary to
analyze clearly. Because of social studies, values, traditions. Culture will
provide answers to what the society wants to do. And who will educate who?
These help to find clear answers to the goals or directions of education. (As
illustrated)
1.
จุดมุ่งหมายเป็นตัวกำหนดควบคุมการเลือกและจัดประสบการณ์การเรียนดังนั้น
การกำหนดจุดมุ่งหมายจึงมี 2 ขั้นตอน คือ
ตอนแรกเป็นการกำหนดจุดมุ่งหมายชั่วคราวแล้วจึงหาวิธีการและเกณฑ์จากทฤษฎีการเรียนรู้ปรัชญาการศึกษาและปรัชญาสังคมมากลั่นกรองจุดมุ่งหมายชั่วคราว
เพื่อให้ได้มาเป็นจุดมุ่งหมายที่แท้จริงของหลักสูตร
พื้นฐานทางจิตวิทยาและปรัชญาในการพัฒนาหลักสูตรจะเข้ามามีบทบาทและช่วยในการตรวจสอบเพื่อหาความชัดเจนของการกำหนดจุดมุ่งหมายขั้นนี้เพื่อตอบคำถามและหาความชัดเจนว่าการจัดหลักสูตรเพื่อตอบสนองใคร
ตอบสนองผู้เรียนหรือสังคม
2.
การเลือกและจัดประสบการณ์การเรียนที่คาดหวังว่าจะให้ผู้เรียนมีประสบการณ์การจัดกิจกรรมในการเรียนการสอนและส่วนเสริมหลักสูตรนั้นมีอะไร
ทั้งนี้เพื่อให้กระบวนการเรียนการสอนดำเนินไปเพื่อตอบสนองจุดมุ่งหมายที่กำหนดไว้ ไทเลอร์ได้เสนอเกณฑ์ในการพิจารณาเลือกประสบการณ์การเรียนรู้ไว้ดังนี้
2.1
ผู้เรียนควรมีโอกาสฝึกพฤติกรรมและการเรียนรู้เนื้อหาตามที่ระบุไว้ในจุดมุ่งหมาย
2.2
กิจกรรมและประสบการณ์นั้นทำให้ผู้เรียนพอใจปฏิบัติการเรียนรู้อาจนำไปสู่จุดมุ่งหมายที่กำหนดไว้เพียงข้อเดียวก็ได้
2.3
กิจกรรมและประสบการณ์นั้นอยู่ในข่ายความพอใจที่พึงปฏิบัติได้
2.4
กิจกรรมและประสบการณ์หลายๆ
ด้านของการเรียนรู้อาจนำไปสู่จุดมุ่งหมายที่กำหนดไว้เพียงข้อเดียวก็ได้
2.5
กิจกรรมและประสบการณ์เรียนรู้เพียงหนึ่งอย่างอาจตรวจสอบจุดมุ่งหมายหลายๆ ข้อได้
3.
การจัดประสบการณ์การเรียนรู้ว่าต้องคำนึงถึงความสัมพันธ์ในด้านเวลาต่อเวลา และเนื้อหาต่อเนื้อหา เรียกว่าความสัมพันธ์แบบแนวตั้ง (Vertical)
กับแนวนอน (Horizontal) ซึ่งมีเกณฑ์ในการจัดดังนี้
3.1
ความต่อเนื่อง (Continuity) หมายถึงความสัมพันธ์ในแนวตั้งของส่วนองค์ประกอบหลักของตัวหลักสูตรจากระดับหนึ่งไปยังอีกระดับหนึ่งที่สูงขึ้นไป
เช่น ในวิชาทักษะ ต้องเปิดโอกาสให้มีการฝึกทักษะในกิจกรรมและประสบการณ์บ่อยๆ
และต่อเนื่องกัน
3.2
การจัดช่วงลำดับ(Sequence) หมายถึงความสัมพันธ์แนวตั้งของส่วนองค์ประกอบหลักของตัวหลักสูตรจากสิ่งที่เกิดขึ้นก่อนไปสู่สิ่งที่เกิดขึ้นภายหลัง
หรือจากสิ่งที่มีความง่ายไปสู่ที่มีความยาก ดังนั้น
การจัดกิจกรรมและประสบการณ์ให้มีการเรียงลำดับก่อนหลังเพื่อให้ได้เรียนเนื้อหาที่ลึกซึ้งยิ่งขึ้น
3.3
บูรณาการ (Integration) หมายถึง
ความสัมพันธ์กันในแนวนอนขององค์ประกอบหลักของตัวหลักสูตร
จากหัวข้อเนื้อหาหนึ่งไปยังอีกหัวข้อหนึ่งของรายวิชา
หรือจากรายวิชาหนึ่งไปยังรายวิชาอื่นๆ ที่มีความเกี่ยวข้องกัน การจัดประสบการณ์จึงควรเป็นในลักษณะที่ช่วยให้ผู้เรียนได้เพิ่มพูนความคิดเห็นและได้แสดงพฤติกรรมที่สอดคล้องกัน
เนื้อหาที่เรียนเป็นการเพิ่มความสามารถทั้งหมดของผู้เรียนที่ได้ประสบการณ์ในสถานการณ์ต่างๆ
กัน ประสบการณ์การเรียนรู้จึงเป็นแบบแผนของปฏิสัมพันธ์ (Interaction) ระหว่างผู้เรียนกับสถานการณ์สิ่งแวดล้อม
4.
การประเมินผลเพื่อตรวจสอบดูว่าการจัดการเรียนการสอนได้บรรลุตามจุดมุ่งหมายตามที่กำหนดไว้หรือไม่ สมควรมีการปรับแก้ในส่วนใดบ้าง พิจารณาจากสิ่งต่อไปนี้
4.1 กำหนดจุดมุ่งหมายที่จะวัดและพฤติกรรมที่คาดหวัง
4.2
วัดและวิเคราะห์สถานการณ์ที่ทำให้เกิดพฤติกรรมเหล่านั้น
4.3
ศึกษาสำรวจข้อมูลเพื่อสร้างเครื่องมือวัดพฤติกรรมเหล่านั้นได้อย่างเหมาะสม
4.4
ตรวจสอบคุณภาพของเครื่องมือ โดยใช้เกณฑ์ในการพิจารณาดังนี้
1.
ความเป็นปรนัย (Objectivity)
2.
ความเชื่อมั่นได้ (Reliability)
3.
ความเที่ยงตรง (Validity)
4.
ความถูกต้อง (Accuracy)
4.5
การพิจารณาผลประเมินให้เป็นประโยชน์เพื่ออธิบายผลการเรียนรู้เป็นรายบุคคลหรือเป็นกลุ่ม
การอธิบายถึงส่วนดีของหลักสูตรหรือสิ่งที่ต้องปรับแก้เพื่อเป็นแนวทางในการปรับปรุงหลักสูตรให้มีคุณภาพยิ่งขึ้น
1. The aim
is to regulate the selection and organization of the learning experience. There
are two steps to set goals: first, to set a temporary goal, then to find the
methods and criteria from learning theory, philosophy, education, and social
philosophy. To get a real purpose of the course. The psychological and
philosophical basics of curriculum development will play a role and help to
determine the clarity of this goal setting in order to answer the question and
to find out exactly who the curriculum is. Meet the learner or society.
2. Selecting and organizing learning experiences
that are expected to give the student experience in teaching and enriching the
course. In order to make the learning process go according to the intended
purpose. Tyler offers the following criteria for selecting learning
experiences:
2.1
Learners should have the opportunity to practice behavior and learn the content
as stated in the intended purpose.
2.2
Activities and experiences enable the learner to enjoy learning, may lead to
one goal only.
2.3
Activities and experiences are subject to satisfactory behavior.
2.4
Activities and experiences The field of learning may lead to one set of goals.
2.5
Activity and one learning experience may examine several purposes.
3. A
learning experience that takes into account time-to-time relationships. And content
to content. It is called vertical relationship (Vertical) with horizontal
(Horizontal), which has the following criteria.
3.1
Continuity means the vertical relationship between the main components of the
curriculum from one level to the next, such as the skill level, the opportunity
to practice the skills in the activity and the experience often. And
consecutive
3.2
Sequence means the vertical relationship of the major components of the course
from what happened before to what follows. From the simplest to the more
difficult, organize activities and experiences in advance ordering to get a
deeper content.
3.3 Integration means
the horizontal relationship of the main components of the curriculum. From one
topic to another. Or from one course to another. Relevant The experience should
be in a way that helps learners to improve their opinions and behave
accordingly. Learning content enhances the ability of all learners to
experience different situations. The learning experience is a pattern of
interaction. Interaction between students and the environment.
4. Evaluation to determine whether the teaching and
learning has met the intended purpose. What are the modifications? Consider the
following:
4.1
Determine the purpose to measure and the expected behavior.
4.2
Measure and analyze the situation that causes those behaviors.
4.3
Investigate the data to create appropriate behavioral measurement tools.
4.4
Check the quality of the tool The criteria are as follows.
1.
Multiple-choice (Objectivity)
2.
Confidence (Reliability)
3.
Validity
4.
Accuracy
4.5 The results of the
evaluation are useful to explain the results individually or in groups.
Describe the good part of the course or what needs to be adjusted to improve
the curriculum.
รูปแบบการพัฒนาหลักสูตรตามแนวความคิดของทาบา
(Taba)
แนวคิดของทาบาในการพัฒนาหลักสูตรใช้วีแบบรากหญ้า
(Grass-roots
approach) มีความเชื่อว่าหลักสูตรควรได้รับการออกแบบโดยครูผู้สอนมากกว่าพัฒนาจากองค์กรที่อยู่ในระดับสูงขึ้น
ประกอบด้วยขั้นตอนต่างๆ ดังนี้ (Taba, 1962 : 456-459)
Taba's conceptual model of development
Grass-roots approach
The development of the Grass-roots approach is believed to be designed by
teachers rather than by higher-level organizations. Contains the following
steps: (Taba, 1962: 456-459)


ไม่มีความคิดเห็น:
แสดงความคิดเห็น